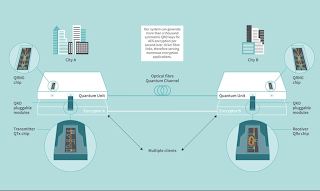
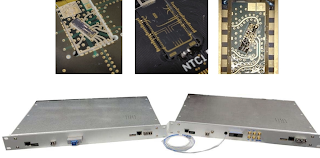
Researchers at Toshiba Europe have developed the world’s first chip-based quantum key distribution (QKD) system, potentially paving the way for much more secure networks.
QKD systems typically comprise a complex fibre-optic circuit, integrating discrete components, such as lasers, electro-optic modulators, beam-splitters and fibre couplers. This project aimed to develop a QKD system on a single chip. Random bits for preparing and measuring the qubits are produced in quantum random number generator (QRNG) chips and converted in real-time into high-speed modulation patterns for the chip-based QKD transmitter (QTx) and receiver (QRx) using field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs). Photons are detected using fast-gated single photon detectors. Sifting, photon statistics evaluation, time synchronisation and phase stabilisation are done via a 10 Gbps optical link between the FPGA cores, enabling autonomous operation over extended periods of time. As part of the demonstration, the chip QKD system was interfaced with a commercial encryptor, allowing secure data transfer with a bit rate up to 100 Gbps.
To promote integration into conventional communication infrastructures, the QKD units are assembled in compact 1U rackmount cases. The QRx and QTx chips are packaged into C-form-factor-pluggable-2 (CFP2) modules, a widespread form-factor in coherent optical communications, to ensure forward compatibility of the system with successive QKD chip generations, making it easily upgradeable. Off-the-shelf 10 Gbps small-form-factor pluggable (SFP) modules are used for the public communication channels.
Andrew Shields, Head of Quantum Technology at Toshiba Europe, remarked, “Photonic integration will allow us to manufacture quantum security devices in volume in a highly repeatable fashion. It will enable the production of quantum products in a smaller form factor, and subsequently allow the roll out of QKD into a larger fraction of the telecom and datacom network.”
Taro Shimada, Corporate Senior Vice President and Chief Digital Officer of Toshiba Corporation comments, “Toshiba has invested in quantum technology R&D in the UK for over two decades. This latest advancement is highly significant, as it will allow us to manufacture and deliver QKD in much larger quantities. It is an important milestone towards our vision of building a platform for quantum-safe communications based upon ubiquitous quantum security devices.”
http://www.quantum.toshiba.co.uk
BT and Toshiba to build quantum-secured metro network across London
BT and Toshiba are to build a quantum-secured metro network linking sites in London’s Docklands, the City and the M4 Corridor. The two companies’ initial focus will be to provide trials for enterprise customers who are carrying sensitive traffic (such as database backups) between sites, and to explore potential future offerings such as encrypted links and “quantum keys-as-a-service." A timeline has not been disclosed.
BT will provide data services secured using Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) and Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) over Openreach’s Optical Spectrum Access Filter Connect (OSA FC) solution for private fibre networks. The QKD links will be provided using a quantum network that includes both core and access components, and will be integrated into BT’s existing network management operations.
Toshiba will provide quantum key distribution hardware and key management software. The company launched commercial products for QKD, manufactured at its Cambridge site, in the latter half of 2020. Toshiba says it has achieved the highest key rates (1,000’s of keys per second) and longest range of any commercially available fibre QKD system.
While BT and Toshiba have previously installed a point-to-point quantum-secure link between two commercial sites, deploying a full quantum-secured metro network environment with multiple endpoints requires new approaches to integration and management.
Building on the BT and Toshiba point-to-point solution for the Bristol-based NCC (National Composites Centre) and Centre for Modelling and Simulation (CFMS), this new network will extend the solution to serve multiple customers across the London metropolitan area.
Howard Watson, CTO of BT, said: “BT and Toshiba have established a global lead in the development of quantum-secure networks. We’re excited to be taking this collaboration to the next level by building the world’s first commercially operational quantum-secured metro network in London. Secure, robust and trusted data transfer is increasingly crucial to our customers across the globe, so we’re proud of the role our Quantum R&D programme is playing in making the world’s networks safer as we enter the dawn of a new age of quantum computing.”
Taro Shimada, Corporate Senior Vice President and Chief Digital Officer at Toshiba Corporation, said: “Our partnership with BT will allow us to offer organisations quantum-secured network services which protect their data from retrospective attacks with a quantum computer. We are delighted to work with BT, with its long heritage of delivering secure, trusted networks. This network paves the way for commercial QKD services in the UK and eventually beyond.”
ADVA FSP 3000 powers UK’s first quantum network

Toshiba Research, BT and ADVA Test ‘Quantum Leap’ Encryption